Platinum Resistance Thermometers Specification
A Pt100 is a sensor used to measure temperature. It is one type of sensor which falls into a group called Resistance Temperature Detectors or RTDs.
The specification of Pt100 temperature sensors is determined by a number of factors and what follows will describe each of the factors and enable you to specify a Pt100 temperature sensor with ease. Of course, if you need any assistance our engineers are always available to assist. Please contact us with your enquiry.

PT-100 sensor
by Process Parameters
Sensor Characteristics
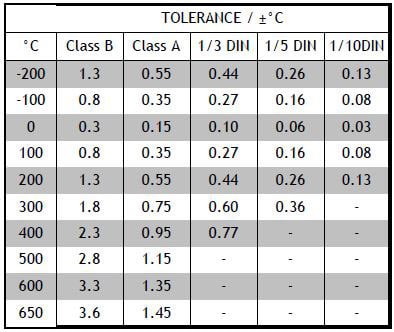
The Pt100 temperature sensor specification is heavily driven by how the sensor works and its characteristics. The Pt100 sensor falls into a group of sensors called Resistance Temperature Detectors or RTDs and they all work on the principle of a change of electrical resistance with changing temperature.
A Pt100 is just one of a range of different sensors and it is important to understand the meaning of this terminology in order to properly specify a Pt100 RTD.
The first of the model number, Pt, is the chemical symbol for Platinum and this is the electrical conductor material used in the sensing element itself. The second part, 100, relates to the resistance value of the sensor at 0°C. In this case 100Ω. There are a number of different types of sensor and they are all specified in a similar way. Different materials can be used such as Nickel (Ni) and Copper (Cu) and different resistance values such as 50Ω, 500Ω and 1000Ω. This gives the possibility of sensors being identified Cu100, Ni120 or Pt1000.
The Pt100 variant is, however, the most commonly used. Sensors using Platinum are also by far the most common group and are often referred to as Platinum Resistance Thermometers or PRTs.
In addition to the base resistance value at 0°C, it is important to understand the resistance change characteristics for the sensor and these should be matched to the instrument you are using. Almost without exception, industrial Pt100 temperature sensors are specified to operate with a coefficient of 3.851×10-3 °C-1 as determined by the international standard IEC 60751:2008. This gives a nominal resistance at 100°C of 138.51Ω.
In addition to this standard set of characteristics, there are others available and used in relatively rare circumstances. Often Process Parameters can supply temperature sensors with these special characteristics so please contact us with your requirement.