Browse our selection of highly reliable wireless transmitters, receivers, and WiFi temperature sensors designed for various industrial applications. Enhance operational efficiency and flexibility with our robust wireless solutions. Perfect for challenging environments and critical processes.
If you have questions about the best wireless transmitter for your industrial needs or require a quote on any of our wireless devices, please get in touch with our experienced team. Our technical specialists are here to help you find the optimal solution.
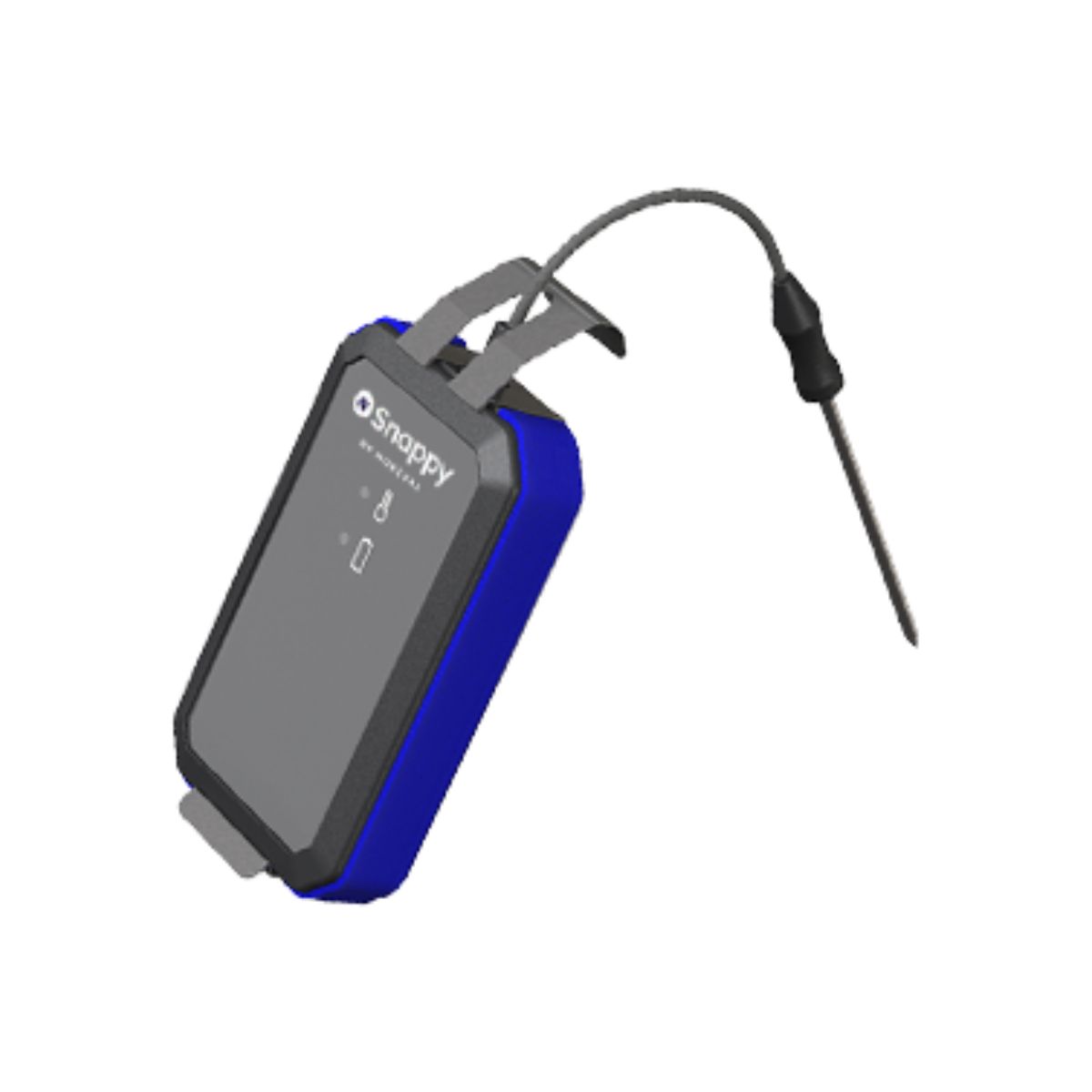
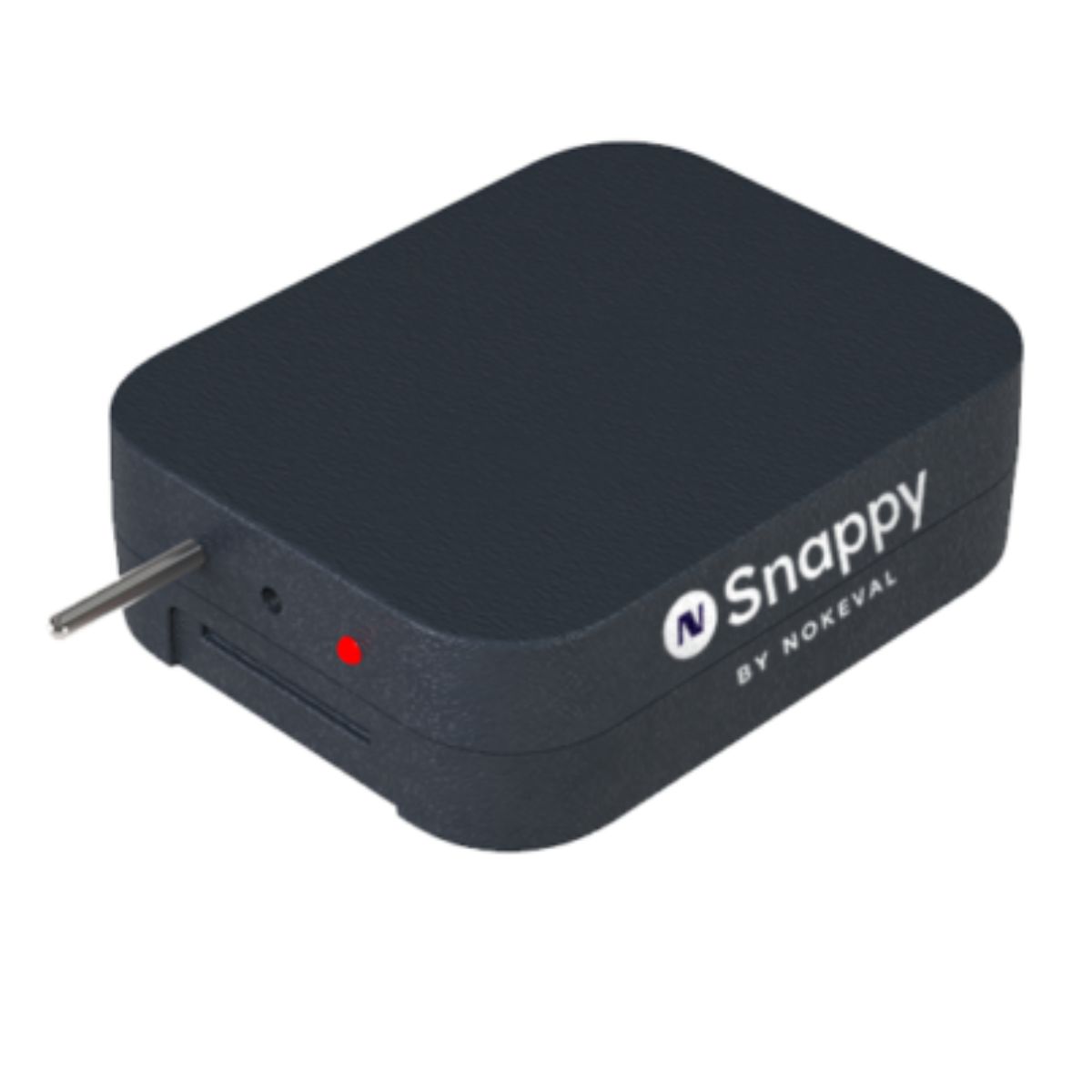
Looking to digitally improve your kitchen and restaurant’s self-monitoring? With NSnappy’s food production probes and sensors, you can enhance efficiency and safety in your kitchen operations. Read more about the NSnappy wireless monitoring service here.
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers For Robust Process Monitoring
Discover our cutting-edge range of wireless transmitters, receivers, and temperature sensors, engineered for unwavering, reliable performance in industrial environments across the UK and Ireland.
Eliminate the limitations of traditional wiring and gain the power of real-time, actionable data for optimised operations and informed decision-making. Streamline your process control and reduce downtime.
Key Advantages of Industrial Wireless Solutions For Your Business:
- Enhanced Flexibility: Install sensors and transmitters in previously inaccessible locations without the constraints of cabling, enabling monitoring in remote or hazardous areas.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Reduce installation time and costs, streamline maintenance, and minimise downtime. Boost your overall productivity.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Access critical temperature and other process data remotely, enabling proactive adjustments and faster issue resolution. Gain immediate insights into your critical parameters.
- Scalability for Growth: Easily expand your monitoring network as your industrial processes evolve and grow. Future-proof your infrastructure.
- Reduced Wiring Complexity: Simplify system design and reduce potential points of failure associated with extensive wiring. Lower installation headaches and maintenance burdens.
Our Comprehensive Industrial Wireless Product Range:
- Robust Industrial WiFi Transmitters: Dependable and secure wireless data transmission for demanding industrial settings. Designed for harsh environments.
- Precise Wireless Temperature Transmitters: Accurate and reliable temperature monitoring for critical industrial processes and HVAC systems. Ensure process integrity and compliance.
- Long-Range WiFi Receivers: Ensure seamless connectivity across large industrial facilities and remote locations. Maximise signal integrity across your site.
- Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN): Create interconnected systems for comprehensive data acquisition and analysis across your plant. Build a truly smart factory.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) WiFi Transmitters: Enable seamless integration of sensors and devices with cloud-based industrial IoT platforms. Leverage the power of IIoT for predictive maintenance and optimisation.
- Wireless Data Transmission Solutions: Secure and efficient transfer of critical process data over wireless networks. Protect your valuable operational data.
Ready to Modernise Your Industrial Monitoring Infrastructure?
Our team of experts is ready to help you identify the ideal wireless solution to optimise your specific industrial processes. We offer personalised advice, competitive pricing, and dedicated technical support. We understand the unique challenges of industrial applications.
Don’t miss the opportunity to enhance the efficiency, flexibility, and data accessibility of your industrial operations with our advanced wireless technology. Contact us today for a free consultation and quote. Let us help you achieve your operational goals.
Call us at 01628 778788 or email sales@processparameters.co.uk
FAQs
What is an Industrial Wireless Transmitter?
An industrial wireless transmitter is a device that sends process data or signals, such as temperature, pressure, or flow, without physical connections. It uses technologies like radio waves, infrared, or Bluetooth to transmit information to a compatible receiver or another device, enabling wireless communication in various applications like remote process control, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking within industrial settings.
What is a Wireless Transmitter and Receiver System?
A wireless transmitter and receiver system are components of a communication system that exchange data without physical connections. The transmitter sends signals or data wirelessly, typically using radio waves or infrared, while the receiver captures and interprets these signals, enabling wireless communication between devices, such as industrial sensors, control systems, and data acquisition platforms.
What is the Difference Between an Industrial Transmitter and an Industrial Receiver?
An industrial transmitter sends data or signals from a sensor or process point, while an industrial receiver receives and interprets those signals. Transmitters initiate communication, like a temperature sensor broadcasting its reading, while receivers capture and process the transmitted information, like a data logger or PLC collecting and displaying that temperature data.
Key Applications for Wireless Sensors and WiFi Transmitters in Industry:
Wireless transmitters and sensors have numerous applications, including:
- Industrial Monitoring: They are used to monitor variables like temperature, pressure, humidity, level, and flow in factories and plants. Crucial for process control and quality assurance.
- Environmental Monitoring: For tracking air quality, weather conditions, and pollution levels within industrial complexes or remote sites.
- Home Automation: Controlling smart home devices, such as thermostats, lights, and security systems. (While not strictly industrial, showcases the underlying technology.)
- Healthcare: Wireless medical sensors monitor patient vital signs and transmit data to healthcare providers. (Again, for broader context of wireless applications.)
- Asset Tracking: Used in logistics to monitor the location and condition of assets like vehicles and cargo. Optimise your supply chain.
- Agriculture: To monitor soil moisture, crop conditions, and livestock health. Enable precision farming.
- Energy Management: For optimising energy usage in buildings and utilities. Drive energy efficiency.
- Automotive: Wireless sensors are crucial in modern cars for various functions, including tire pressure monitoring and collision avoidance.
- Consumer Electronics: In wireless headphones, gaming controllers, and remote controls.
- IoT (Internet of Things) and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things): Enabling interconnected devices for various applications like smart cities and connected appliances, extending to smart factories and predictive maintenance in industrial settings.
For more information, read our in-depth wireless environmental monitoring system guide.
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
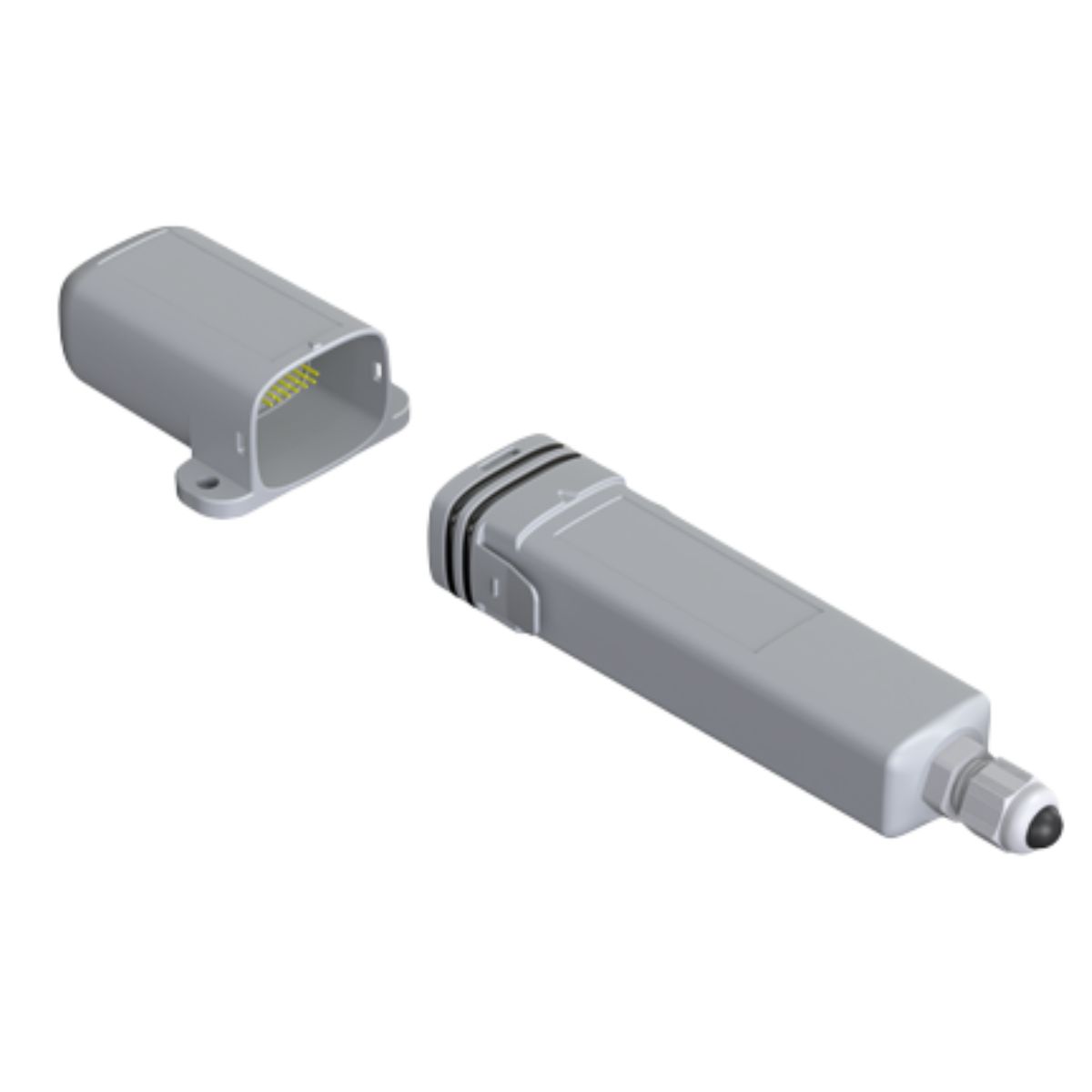
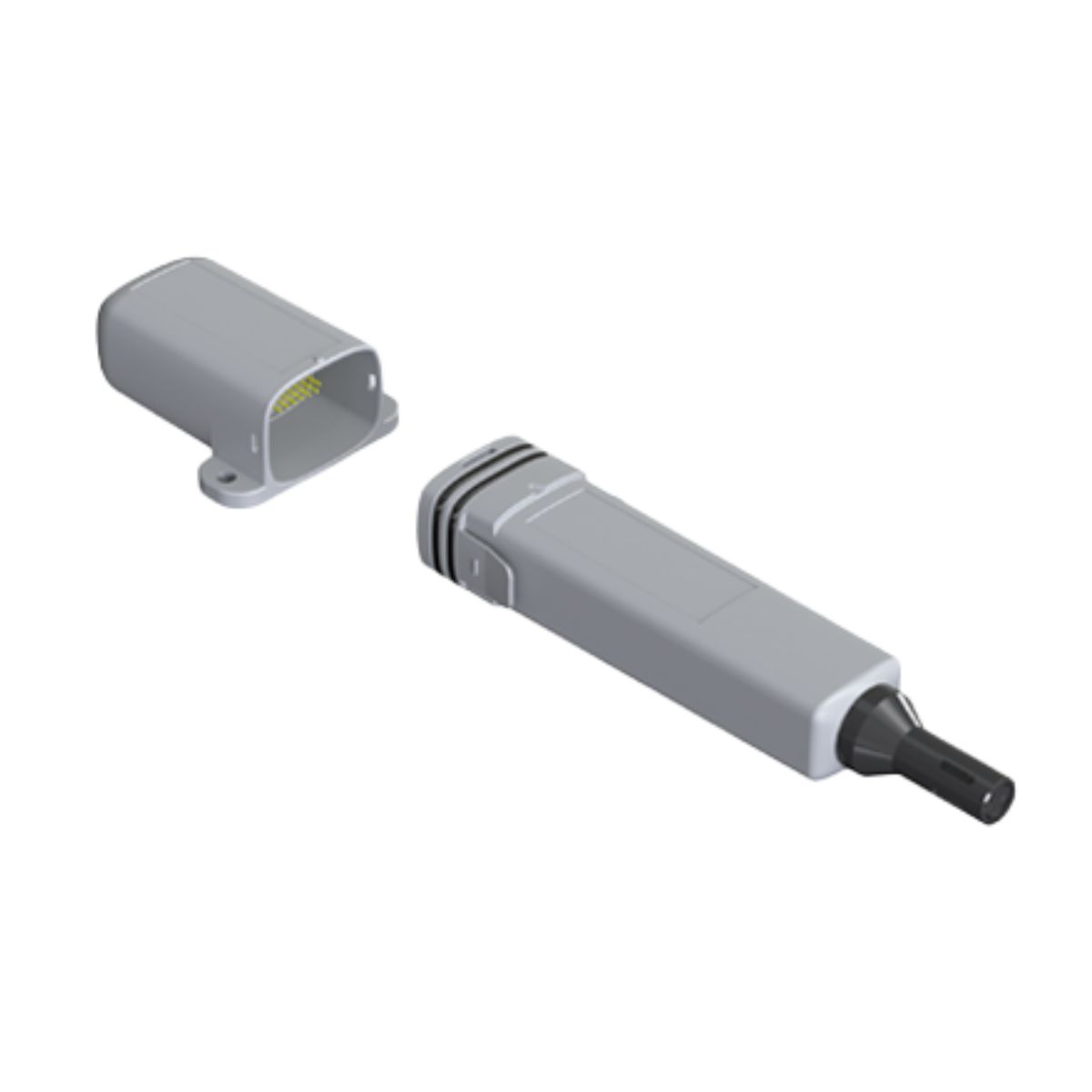
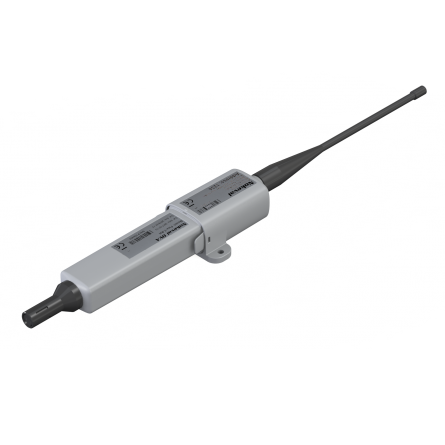
Nokeval Flex2-T-RH LWEU/LWNA Temperature & Humidity Transmitter Sensor
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
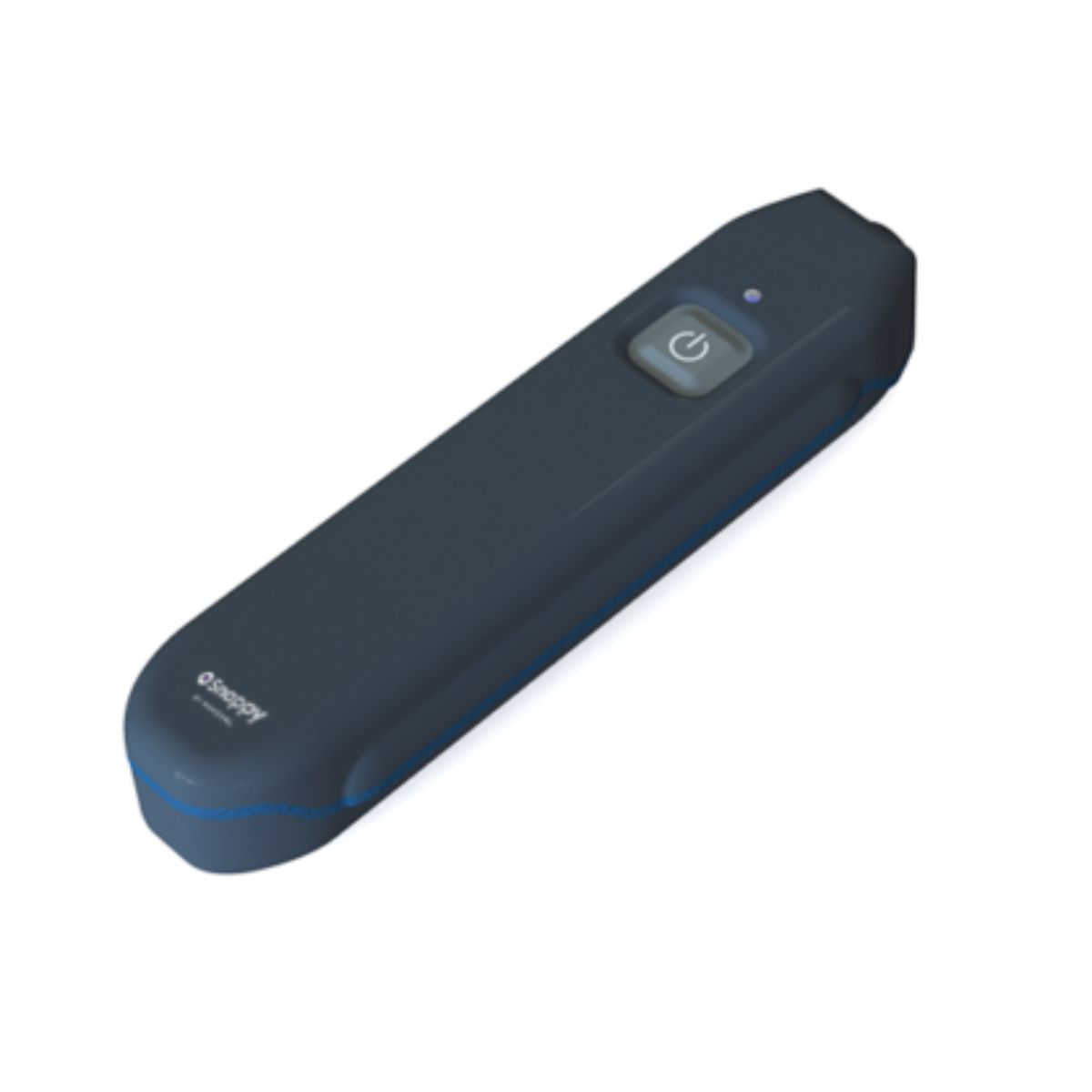
NSnappy Sense IR LWEU-N Infrared Food Service Thermometer Sensor
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
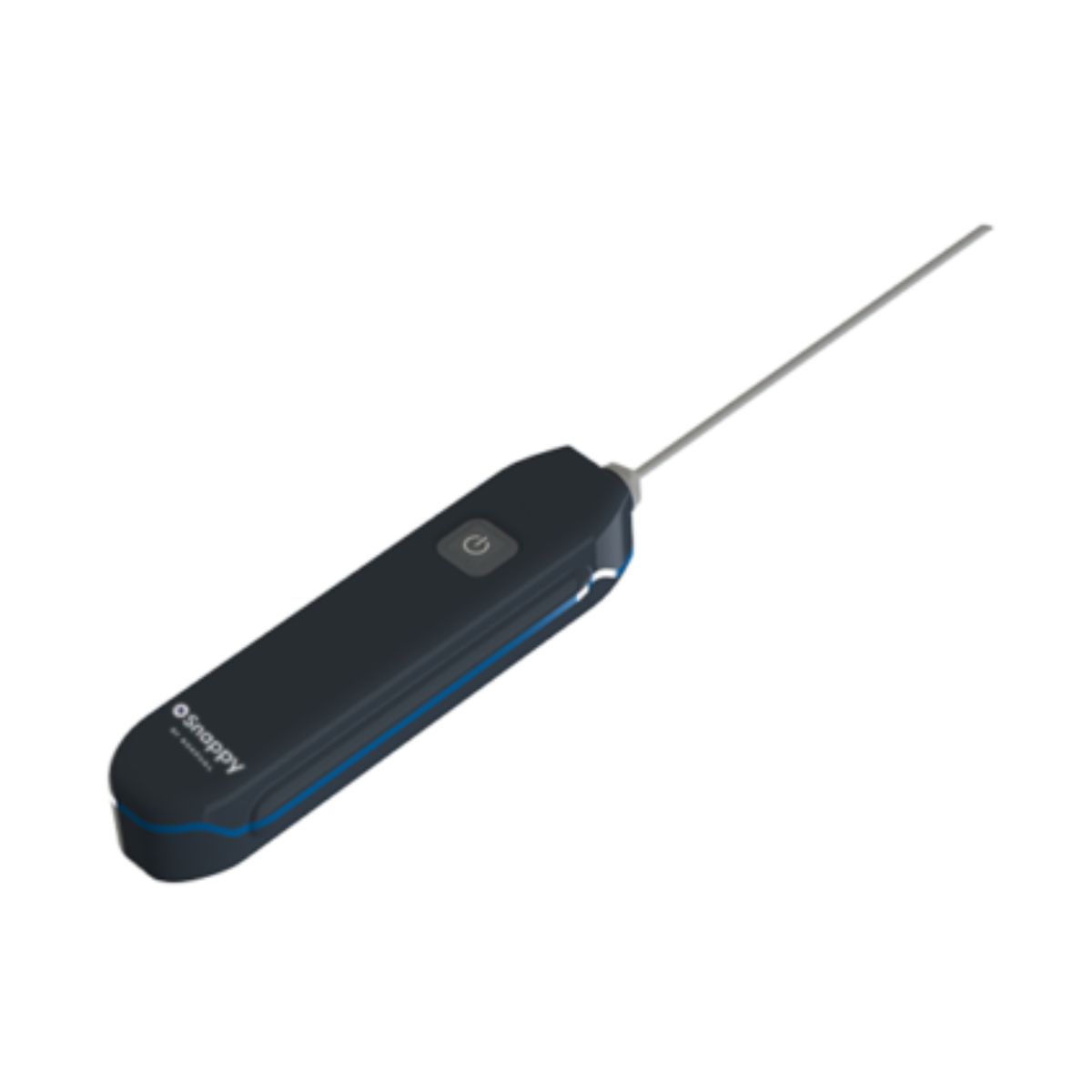
Nokeval Wireless Infrared (IR) Temperature Sensor with Bluetooth
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
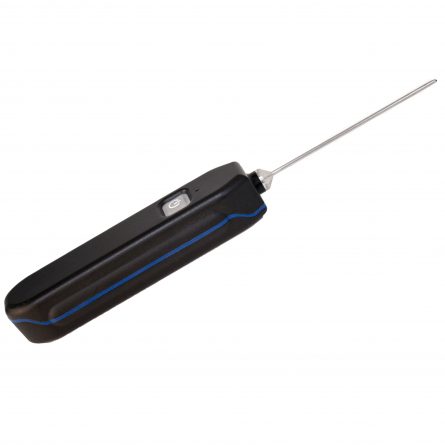
Nokeval Bluetooth Thermometer Pt100 Temperature Sensor Probe
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Nokeval Wireless Data Receiver and Repeater for Transmitters
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Nokeval Wireless Temperature, Humidity, CO2, TVOC, & Pressure Transmitter
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Nokeval Humidity, Temperature & Particle Concentration Wireless Transmitter
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Industrial Wireless Temperature Sensors, Transmitters & Receivers
Flex-Sky-T Wireless Temperature Transmitter with Pt100 Sensor