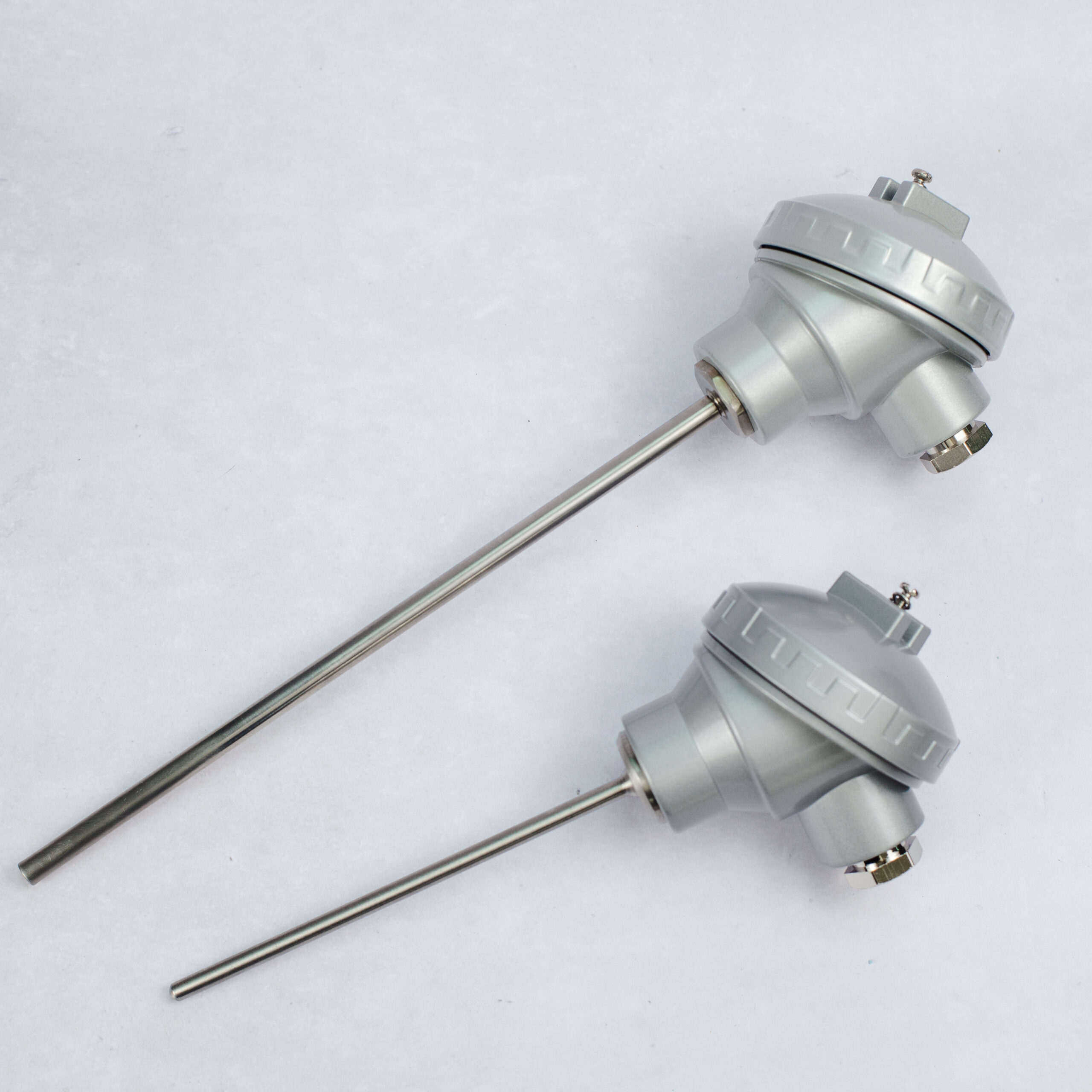
Understanding RTD Connections: Difference Between 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire RTDs
What is a 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire RTD Connection?
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) come with different connection configurations—2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire.
RTDs are widely used due to their accuracy and reliability. However, the different types of RTD offer varying levels of precision and application suitability.
In this article, we will explore these RTD connections in detail, helping you understand the differences and choose the right configuration for your needs.
Did you know that we design and manufacture custom-built resistance thermometers? If you’re not sure what you need, please get in touch and we can help identify your requirements.
Contact Our TeamPlatinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
RTD Pt100 Temperature Sensor PPL3-P, IP68 KNE Terminal Head, 4-20mA Transmitter
Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
What is an RTD Sensor?
An RTD sensor, or Resistance Temperature Detector, is a device used to measure temperature. An RTD probe works by sensing the change in the electrical resistance of a metal wire as the temperature changes.
This change in resistance is then converted into a temperature reading, providing high accuracy temperature measurements in various applications and industries.
Read more about ‘what is an RTD sensor?‘ here.
Difference Between 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire RTDs
The difference between 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire RTD connections lies in how they handle lead resistance. 2-Wire includes lead resistance in the measurement, 3-Wire compensates for it, and 4-Wire eliminates it for the most accurate readings.
Here are some comparisons:
Accuracy Comparison
- 2-Wire RTDs: Less accurate due to the impact of lead wire resistance.
- 3-Wire RTDs: Improved accuracy as the third wire compensates for some of the lead wire resistance.
- 4-Wire RTDs: Offers the highest accuracy by completely eliminating the impact of lead wire resistance.
Cost and Complexity
- 2-Wire RTDs: Least expensive and simplest to install.
- 3-Wire RTDs: A balance between cost and accuracy, with moderate installation complexity.
- 4-Wire RTDs: Most expensive and complex, but provides the best precision.
Application Scenarios
- 2-Wire RTDs: Best for short-distance measurements and less critical applications where cost is a primary concern.
- 3-Wire RTDs: Suitable for industrial applications where moderate accuracy is needed and lead wire resistance could affect measurements.
- 4-Wire RTDs: Ideal for high-precision environments such as laboratories or critical industrial processes where accuracy is paramount.
At Process Parameters, our RTD sensors are ideal for general-purpose industrial and OEM applications. We’re able to manufacture our resistance thermometers to your requirements for almost any environment.
Take a look at the industries we work with.
How to Choose the Right RTD Configuration for Your Needs
When selecting an RTD configuration, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy Requirements: Higher accuracy needs may warrant a 3-wire or 4-wire RTD.
- Distance Between Sensor and Measurement Device: Longer distances typically require 3-wire or 4-wire RTDs to minimise errors.
- Budget Constraints: Balance the need for accuracy with your budget by choosing the appropriate RTD configuration.
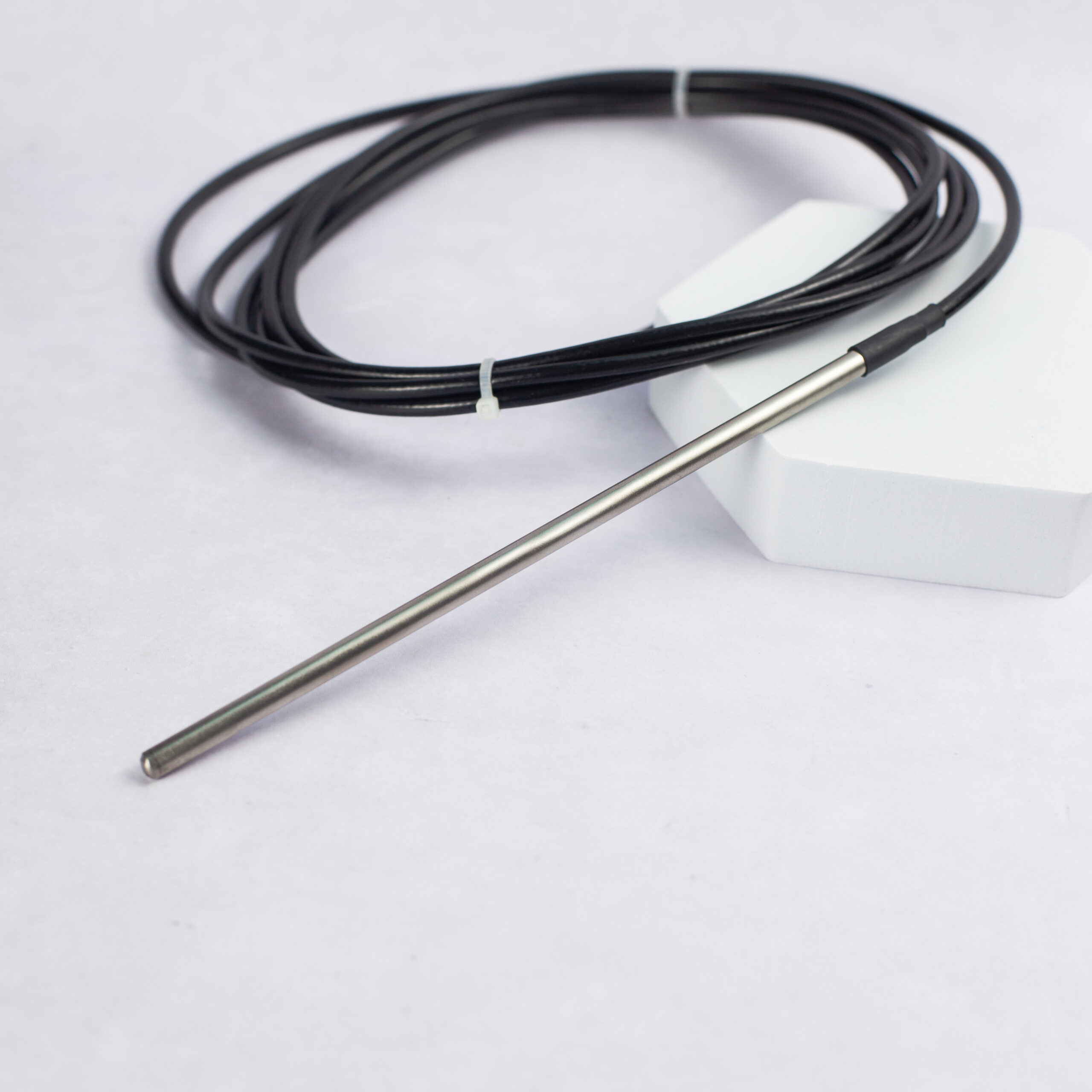

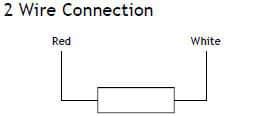
Understanding 2-Wire RTD Connections
What is a 2-Wire RTD?
A 2-wire RTD configuration is the simplest type of RTD setup. It consists of two wires connecting the RTD element to the measurement device. This configuration is often used in less demanding applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities.
Advantages of 2-Wire RTDs
- Simplicity: The 2-wire setup is straightforward and easy to install, making it an economical choice for many applications.
- Cost-Effective: Due to fewer components, 2-wire RTDs are generally less expensive than their 3-wire and 4-wire counterparts.
- Suitable for Short Distances: Ideal for applications where the sensor and measurement device are close together.
Disadvantages of 2-Wire RTDs
- Measurement Error: The resistance of the lead wires can affect accuracy, especially in longer cable runs.
- Limited Accuracy: Not suitable for high-precision measurements due to potential errors introduced by lead wire resistance.
Exploring 3-Wire RTD Connections
What is a 3-Wire RTD?
A 3-wire RTD connection includes an additional wire compared to the 2-wire setup. This third wire is used to measure and compensate for the resistance of the lead wires, which improves the accuracy of the temperature measurement.

Advantages of 3-Wire RTDs
- Improved Accuracy: The third wire helps to correct for lead wire resistance, offering better accuracy than the 2-wire configuration.
- Common Use: Widely used in industrial applications where moderate accuracy is required and where lead wire resistance can impact measurements.
- Cost-Effective Accuracy: Balances cost and performance effectively, making it a popular choice for many temperature measurement tasks.
Disadvantages of 3-Wire RTDs
- Potential for Error: While more accurate than 2-wire RTDs, some measurement errors can still occur, particularly in very long cable runs.
- Complexity: Slightly more complex than 2-wire RTDs, which can add to installation time.
The Precision of 4-Wire RTD Connections
What is a 4-Wire RTD?
A 4-wire RTD configuration is designed for the highest level of accuracy. It uses two pairs of wires: one pair for carrying current and the other for measuring voltage. This setup completely eliminates the influence of lead wire resistance on the temperature measurement.

Advantages of 4-Wire RTDs
- Highest Accuracy: By measuring the voltage drop across the RTD element directly, the 4-wire configuration provides the most accurate temperature readings.
- Ideal for Precision Applications: Perfect for laboratory and high-precision industrial applications where accuracy is critical.
- Compensates for Lead Wire Resistance: Ensures that lead wire resistance does not affect the measurement accuracy.
Disadvantages of 4-Wire RTDs
- Higher Cost: More complex and costly compared to 2-wire and 3-wire RTDs.
- Installation Complexity: Requires careful installation to ensure accuracy, which may involve more time and expertise.
Understanding RTD Connections – Conclusion
Understanding the differences between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire RTDs is essential for selecting the right temperature sensor for your application. Each configuration offers unique advantages and is suited for different levels of accuracy and cost. By carefully considering your specific needs, you can ensure accurate and reliable temperature measurements.
For expert advice on choosing and installing RTDs, contact us today. Our team is ready to help you select the perfect RTD configuration to meet your requirements and ensure optimal performance in your temperature measurement applications.
Email us at sales@processparameters.co.uk, call 01628 778788, or complete our online enquiry form.
Send An EnquiryPlatinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
RTD Pt100 Temperature Sensor PPL3-P, IP68 KNE Terminal Head, 4-20mA Transmitter
Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD Sensor, PRT, Pt100 Sensors, Pt1000)
RTD Connections FAQs
What is the main advantage of a 4-wire RTD over a 2-wire RTD?
The main advantage of a 4-wire RTD is its ability to provide the highest accuracy by completely eliminating the influence of lead wire resistance.
Are 3-wire RTDs more accurate than 2-wire RTDs?
Yes, 3-wire RTDs are more accurate than 2-wire RTDs because they include an additional wire to compensate for lead wire resistance.
When should I use a 2-wire RTD?
A 2-wire RTD is suitable for short-distance measurements and applications where cost is a primary concern, but it may be less accurate than 3-wire or 4-wire RTDs.
How does lead wire resistance affect RTD measurements?
Lead wire resistance can cause measurement errors by adding resistance to the RTD reading. 3-wire and 4-wire configurations help compensate for this resistance to improve accuracy.
What are the differences between 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire RTD configurations?
2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire RTD configurations differ in how they manage lead resistance to ensure accurate measurement of RTD temperature. In a 2-wire circuit, lead resistance is part of the measuring element, potentially affecting accuracy, especially with long lead lengths. 3-Wire configurations use an additional wire to compensate for lead resistance, improving accuracy. 4-wire RTDs use a constant current source and measure the potential difference across the RTD, eliminating lead resistance errors, ideal for precise laboratory applications. Each configuration has its own characteristics and is chosen based on individual user requirements and the specific control instrument.
Related Guides:
- What is an RTD Sensor?
- RTD vs Thermocouples
- What Is A Temperature Sensor?
- Pt100 Wiring Methods – 2, 3 or 4 wire?