Difference Between J vs K Type Thermocouples: Which to Buy?
J Type vs K Type Thermocouple Comparison
When it comes to selecting the right thermocouple wire, you’ll often find yourself deciding between two popular options: Type K and Type J. These two types of thermocouples are favoured for their versatility, reliability, and ability to cater to a wide range of applications, making them the go-to choices for many.
Temperature monitoring plays a crucial role across various industries, ensuring the smooth operation of machinery and equipment. It’s a critical parameter that directly impacts the quality of production output and the integrity of machines.
To achieve precise temperature measurements, one of the widely used instruments is the thermocouple. This device is crafted by joining two dissimilar metallic wires to create a junction. When this junction encounters either hot or cold temperatures, a small voltage is generated, which can be measured to obtain temperature readings.
The type of wire used in the thermocouple determines the range of temperatures it can handle and how accurate the readings will be.
In this article, we will delve into the differences between the J-type and K-type thermocouples, exploring their respective advantages and disadvantages to give you a better understanding of which thermocouple suits your needs best.
And don’t forget, our team of experts at Process Parameters will be able to assist you with choosing the right equipment for your specific applications.
Contact UsWhat is the Difference Between a Type J and Type K Thermocouple
Type K and type J thermocouple wires are both versatile, reliable, and cost-effective options, but they have distinct benefits when it comes to different applications.

What is the Difference Between Type J and K Thermocouples?
The type K Thermocouple cable is typically used in high-temperature applications, corrosive environments, and applications where the cable is prone to oxidation. This includes moisture-prone applications as well as complete submergence in water. The type J cable is popular in vacuum applications, and it’s also commonly used in cold environments.
However, when it comes to obtaining accurate temperature readings, the type J thermocouple has an advantage over the type K due to its superior quality of output. Let’s take a closer look at the comparison between these two types of thermocouples.
Type K Thermocouple
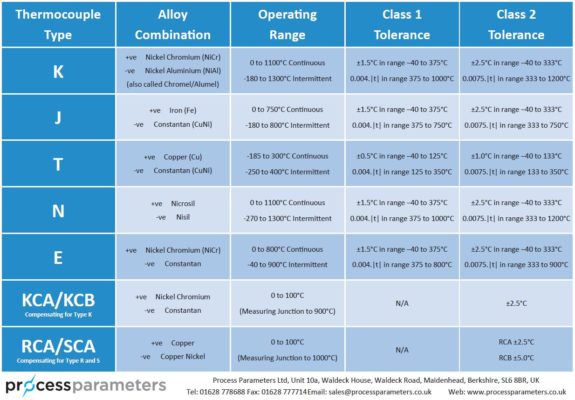
A type K thermocouple consists of nickel/chromium alloy (chrome) and nickel/aluminium alloy (alumel) conductors. This combination grants it excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for work in oxidising atmospheres. It is one of the most versatile thermocouples, with a broad temperature range.
Due to its oxidation resistance, Type K thermocouple wire outlasts the Type J variant. Moreover, it is a fast-response thermocouple, making it ideal for measuring temperatures on surfaces and in liquids.
Applications of Type K Thermocouples
Type K thermocouples are commonly used in applications where temperatures reach 550°C and higher, with a maximum operating temperature of 1100°C. This temperature range encompasses a wide array of industrial processes.
Some common applications of Type K thermocouples include:
- Casting: Monitoring temperatures during low-temperature metal casting processes
- Chemical Refineries: Testing temperatures in various chemical processes
- Petroleum Facilities: Monitoring temperatures in oil-related operations
- Nuclear Plants: Due to its radiation hardening, it’s suitable for nuclear environments
However, Type K thermocouples are not recommended for vacuum-like applications or environments with high sulphur content due to the properties of Chromel and Alumel in such conditions.
Type J Thermocouple
Type J thermocouple wire consists of two conductors: one is made of iron, and the other is a constantan (Copper-Nickel) alloy wire. The temperature range of this cable is from -40°C to 750°C, limited by the properties of iron, which starts to oxidise at higher temperatures.
Type J is more affordable than Type K thermocouple wire, and both types fall within the lower price range compared to other thermocouple grade wires.
This thermocouple type serves as a general-purpose option with a narrower temperature range, suitable for light industry operations with less extreme temperatures. It has iron on the positive leg and copper-nickel alloy on the negative leg.
However, Type J thermocouples are not suitable for temperatures exceeding 750°C (1383°F) due to the iron conductor’s limitations. When exposed to oxidising agents, the iron undergoes irreversible molecular changes, leading to inaccurate temperature readings.
Applications of Type J Thermocouples
Type J thermocouples find their application in the following scenarios:
- Vacuum applications
- Monitoring temperatures of inert materials like sand, concrete, or asbestos-containing materials
- Temperature monitoring during plastics and resin manufacturing
In summary, understanding the differences between type J and type K thermocouples is crucial to ensure their proper use in specific temperature ranges and environments, optimising their performance for various industrial applications.
Thermocouple Sensors for Industrial Applications
Temperature Probes & Sensors
Thermocouple Sensors for Industrial Applications
Thermocouple for Ambient Air Temperature Measurement Sensor – PPL10-T
Temperature Probes & Sensors
Type K vs Type J Thermocouple: Which to Buy?
Aspect | Type J Thermocouple | Type K Thermocouple |
Temperature Range | General purpose thermocouple due to small temperature range | Widest temperature range of the four thermocouple types |
Sensitivity | Lower sensitivity compared to type K | Higher sensitivity compared to type J |
Material Compatibility | Not suitable for oxidising atmospheres | Suitable for oxidising and reducing atmospheres |
Accuracy | Moderate accuracy | High accuracy |
Magnetic Susceptibility | More magnetic interference | Less magnetic interference |
Cost | Generally lower cost | Slightly higher cost |
Application Suitability | Suitable for lower temperature applications | Suitable for a wide range of applications |
Corrosion Resistance | Susceptible to corrosion at higher temperatures | Better corrosion resistance |
Stability | Less stable at higher temperatures | More stable at higher temperatures |
Availability | Commonly available | Widely available |
Please note that the suitability of a thermocouple type depends on the specific requirements of the application. For some scenarios, the advantages of one type might outweigh its disadvantages compared to the other.
Thermocouples from Process Parameters
Process Parameters offer an extensive range of custom-built temperature sensors (Thermocouples, Pt100’s) manufactured to your requirements and application. Get in touch with our team of experts, or view our range of high quality thermocouples.
Process Parameters are on hand to assist you with your thermocouple type queries and product selection, as well as calibration and implementation.
For further information please email us at sales@processparameters.co.uk or call 01628 778788.
Send An EnquiryThermocouple Sensors for Industrial Applications
Temperature Probes & Sensors
Thermocouple Sensors for Industrial Applications
Thermocouple for Ambient Air Temperature Measurement Sensor – PPL10-T
Temperature Probes & Sensors
Related Articles:
- How does a thermocouple work?
- What is a temperature transmitter?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermocouples
- What are type K thermocouples?
- Comparing Contact and Non-Contact Temperature Sensors
- What Is A Temperature Sensor?