What is a Pyrometer? How Do They Work?
How do Pyrometers and Infrared Thermometers Work?
A pyrometer is a type of non-contact temperature sensor that detects heat by measuring the amount of radiation it emits. Pyrometers have been used for centuries to measure the temperature of hot objects, such as molten metal, glass, and flames.
They are also used in a variety of industrial and scientific applications, such as monitoring the temperature of engines, furnaces, and chemical reactions.
We are the leading UK distributor for Optris, a manufacturer of infrared thermometers, pyrometers and thermal imaging cameras for applications such as metals, plastics and glass. Contact our team to discuss your application and find out how a pyrometer temperature sensor can improve your industrial processes.
Contact UsIn this article, we’ll discover ‘what is a pyrometer’, how they work, the uses of pyrometers, and the benefits and limitations of pyrometers.
What is a Pyrometer?
Pyrometers measure temperature by detecting and analysing thermal radiation emitted by an object. When an object is heated, it emits thermal radiation in the form of electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The intensity and wavelength distribution of this radiation depends on the temperature of the object.
How Does a Pyrometer Work?
Pyrometers work by capturing this thermal radiation and converting it into an electrical signal that can be processed and interpreted. The specific method used by a pyrometer depends on its type (optical, infrared, two-colour, or total radiation) and its design.
General Purpose IR Thermometers
General Purpose IR Thermometers
General Purpose IR Thermometers
Types of Pyrometers
- Optical pyrometers use lenses or optical systems to focus the thermal radiation onto a detector, such as a thermopile or a photodiode. The detector converts the radiation into an electrical signal, which is then amplified and analysed. Optical pyrometers often employ the principle of comparing the radiation from the object to that of a reference source, allowing for temperature determination.
- Infrared pyrometers use specialised sensors, such as thermopiles or bolometers, to directly detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by the object. These sensors generate an electrical signal proportional to the intensity of the radiation, which is then processed to calculate the temperature.
Take a look at our guide on Choosing an Infrared Pyrometer for more information.
- Two-colour pyrometers use two different wavelengths of infrared radiation and measure their ratio. The ratio is dependent on the temperature of the object and can be used to calculate the temperature accurately.
- Total radiation pyrometers measure the total amount of heat radiation emitted by an object, taking into account the intensity across a broad range of wavelengths. This comprehensive measurement provides high accuracy but requires more complex technology.
Each type of pyrometer comes with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Optical pyrometers are the oldest type of pyrometer. They are accurate and precise but can be difficult to use and require calibration.
Infrared pyrometers are more accurate than optical pyrometers and can be used to measure the temperature of objects that are not visible to the naked eye. However, they tend to be more expensive than optical pyrometers.
Two-colour pyrometers use two different wavelengths of infrared radiation to measure the temperature of an object. This type of pyrometer is more accurate than single-wavelength pyrometers, but it can be more expensive.
Total radiation pyrometers measure the total amount of heat radiation emitted by an object. This type of pyrometer is the most accurate type of pyrometer, but it can be the most expensive.
Difference Between Pyrometers and IR Cameras
A pyrometer is a type of infrared thermometer. The difference between a pyrometer and an infrared thermometer is that pyrometers can only record the temperature at one point.
This can be compared to an infrared thermometer or thermal imaging camera which provides more information, and can also be used to determine the hottest or coldest point within a measuring area.
Read our guide on high temperature pyrometers for more information.
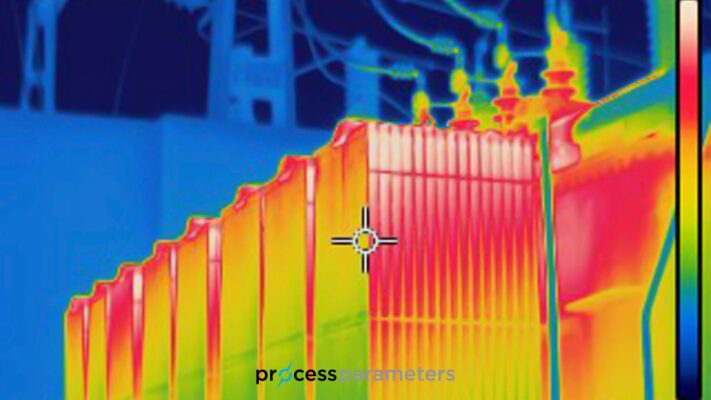
What is a Pyrometer Used For?
Pyrometers find applications in a wide range of industries and scientific fields due to their non-contact temperature measurement capability. Some common uses of pyrometers include:
Industrial processes: Industrial pyrometers are used in manufacturing processes to monitor and control the temperature of materials, such as molten metals, glass, plastics and ceramics. They help ensure proper heating, cooling, and quality control.
Learn more about How to Choose an Infrared Pyrometer for Plastics.
Furnace and kiln monitoring: Pyrometers play a crucial role in monitoring the temperature inside furnaces, kilns, and ovens used in industries like steel, glass, and ceramics. They enable precise temperature control, optimise energy consumption, and ensure product quality.
Power generation: Pyrometers are used in power plants to monitor the temperature of boilers, turbines, and other components. This helps prevent overheating, optimise efficiency, and ensure safe operation.
Automotive industry: Pyrometers are utilised in automotive manufacturing and research for measuring the temperature of engine components, exhaust systems, brakes, and other parts. This aids in performance optimisation, emissions control, and safety.
Research and development: Pyrometers are extensively used in scientific research, particularly in fields such as physics, chemistry, and materials science. They help investigate high-temperature phenomena, study the thermal properties of materials, and enable precise temperature control in experiments.
Firefighting and safety: In firefighting and safety applications, pyrometers are employed to measure the temperature of flames, detect hotspots in buildings or machinery, and assess potential fire hazards.
What are the Benefits of Pyrometers?
Pyrometers offer a number of benefits over other methods of temperature measurement, such as contact thermometers. Some of the benefits of using IR pyrometers include:
- Non-contact temperature measurement: Pyrometers do not need to come into direct contact with the object being measured, which can be hazardous or challenging in some cases.
- Accuracy and precision: Pyrometers can be very accurate and precise, especially when used with a calibrated sensor.
- Wide range of applications: Pyrometers can measure the temperature of a wide range of objects, from molten metal to flames.
Limitations of Using Pyrometers
- Cost: Pyrometers can be more expensive than other types of thermometers.
- Calibration requirements: Pyrometers need to be calibrated regularly to ensure accuracy.
- Environmental factors: Pyrometers can be affected by environmental factors, such as dust and humidity.
Conclusion of What is a Pyrometer
Pyrometers are invaluable tools for non-contact temperature measurement, utilising thermal radiation emitted by objects to determine their temperature. They offer numerous advantages, including non-contact measurement, accuracy, precision, and wide applicability across industries and scientific research. With different types of pyrometers available, each with its own strengths and limitations, the correct choice of a pyrometer depends on the specific requirements.
Our team are always on hand with free technical assistance which is always readily available.
If you would like additional assistance in choosing an infrared temperature sensor, get in touch and we would be glad to discuss your application and help with your product selection.
Contact UsGeneral Purpose IR Thermometers
General Purpose IR Thermometers
General Purpose IR Thermometers
Pyrometer FAQs
What is a pyrometer used for?
Pyrometers are used to measure the temperature of objects without making physical contact. They find applications in industries such as manufacturing, power generation, automotive, and scientific research.
What are the different types of pyrometers?
There are various types of pyrometers, including optical pyrometers, infrared pyrometers, two-colour pyrometers, and total radiation pyrometers. Each type utilises different principles and technologies for temperature measurement.
What is the difference between a thermometer and a pyrometer?
The main difference between a thermometer and a pyrometer lies in the temperature measurement method. Thermometers typically require physical contact with the object being measured, while pyrometers measure temperature remotely using levels of thermal radiation. Pyrometers are suitable for measuring high temperatures or in situations where physical contact is impractical or unsafe.
Related Articles:
- How Does a Thermal Imaging Camera Work?
- How Accurate are Infrared Thermometers?
- Choosing an Infrared Pyrometer
- Can a Thermal Camera See Through Walls?
- How Does an Infrared Thermometer Work?
- Why is a Pin Sharp Thermal Image Important?
- How Can a Thermal Imaging Camera Become Part of Your Process?
- Can You Improve Your Thermal Efficiency With Imaging Cameras?
- Comparing Contact and Non-Contact Temperature Sensors
- What Is A Temperature Sensor?
- Pyrometer or IR Camera?





